Driving pleasure: Instant acceleration and silent operation offer a unique driving experience.
Hybrid vehicles: They combine an electric motor with an internal combustion engine, offering an intermediate step toward electromobility.
Discover the benefits of electromobility and learn how to connect charging infrastructure to the Network.

At HEDNO, we support your transition to electromobility by facilitating the connection of charging infrastructure. Here, you’ll find all the information and instructions you need for the connection process to the Network.
Electromobility offers a variety of options for every mobility need. Today, there is a large number of electric cars, motorcycles, scooters, and bicycles. Regarding cars, consumers can choose among different technologies:
Hybrid vehicles: They combine an electric motor with an internal combustion engine, offering an intermediate step toward electromobility.
Full electric vehicles: They operate exclusively on electric energy, thanks to an integrated battery located at the car’s base.
Fuel cell vehicles: They use hydrogen to generate electricity, ensuring long range. Hydrogen is stored in a high-pressure tank within the vehicle.
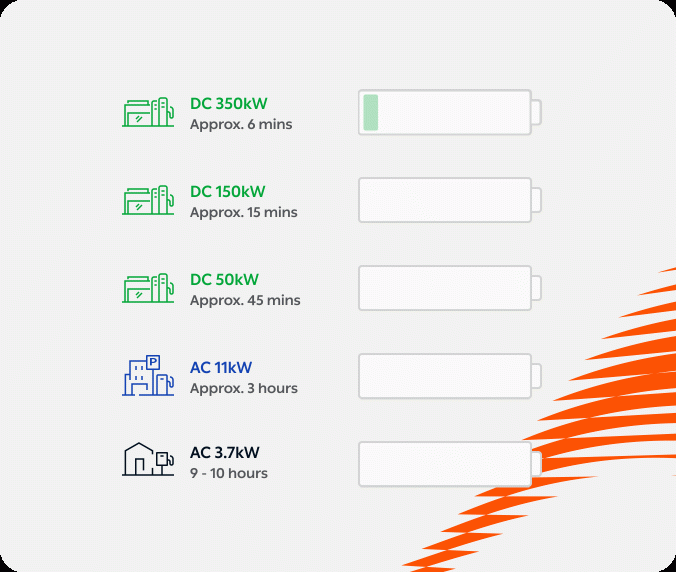
The performance and driving range of electric vehicles largely depend on battery technology, capacity, and individual usage patterns. Below are examples of typical charging systems and the estimated time required to fully recharge the battery:
Charging Time by Charging Power
The time required to charge your battery depends not only on the software of the charging station but primarily on its power. Here you can see the differences in charging times.
Reference scenario: Charging a 58kWh battery from 20% to 80% of its maximum capacity.
Electric vehicle (EV) charging is performed through different types of current and connections, offering flexibility and options depending on your needs.
AC (Alternating Current) Charging
AC charging is based on electricity supplied from the network and converted to direct current (DC) by the vehicle’s onboard charger.
Key characteristics:

DC (Direct Current) Charging
Electricity is delivered directly to a device—such as an electric vehicle or battery—in the form of direct current (DC).
DC charging bypasses the vehicle’s onboard charger and delivers power directly to the battery, enabling significantly faster charging times.
Key characteristics:
Examples of DC fast chargers include Tesla Superchargers, CHAdeMO, and CCS (Combined Charging System).

Download the necessary forms and instructions for the charging infrastructure installation process.
Application/Information for connecting electric vehicle charging infrastructure to a new or existing Low Voltage (LV) supply
Application/Information for connecting electric vehicle charging infrastructure to a new or existing Medium Voltage (MV) supply
Information Note for the Installation of an Electric Vehicle Recharging Infrastructure Metering Device in the Consumer’s Internal Installation
Information Note with Technical Requirements for Connecting Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure to the Electricity Distribution Network in Public Areas through Independent Three-Phase Low Voltage Supplies
Standardization of the construction of a supporting wall for three-phase Low Voltage supplies No. 5, No. 6 and No. 7 in outdoor areas
HEDNO Participation Form in the EVCP (Electric Vehicle Charging Plan) Development Process
Our Frequently Asked Questions section provides clear answers and helpful information on the most common topics and concerns.
If you need any assistance, you can contact us at emobility.support@deddie.gr
